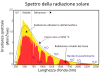
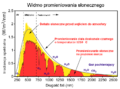
Faịlụ:Solar spectrum en.svg
Ọdịdị

Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 800 × 600 piksels. Ndị ọzọ mkpebi:320 × 240 piksels | 640 × 480 piksels | 1,024 × 768 piksels | 1,280 × 960 piksels | 2,560 × 1,920 piksels.
Failụ si na nke mbu (usòrò SVG, nà áhà pixel 800 × 600, ívụ usòrò: 49 KB)
Ịta nke usòrò
Bìri èhì/ogè k'ị hụ òtù ụ̀fa dị̀ m̀gbè ahụ̀.
| Èhì/Ogè | Mbọ-aka | Ógólógó na asaá | Òjìème | Nkwute | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dị ùgbu â | 16:10, 13 Mee 2019 |  | 800 × 600 (49 KB) | Tuvalkin | It's W, not kW, as further discussed: Reverted to version as of 20:57, 21 February 2016 (UTC) |
| 14:13, 25 Febụwarị 2019 |  | 800 × 600 (49 KB) | Tuvalkin | W → kW, as dicussed | |
| 20:57, 21 Febụwarị 2016 | 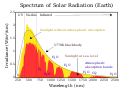 | 800 × 600 (49 KB) | BenRG | Replace 5250°C blackbody (seemingly miscalculated anyway) with standard 5778K blackbody; center-align captions; use Unicode ² instead of SVG superscript to fix rendering problems | |
| 22:21, 7 Jenụwarị 2015 |  | 800 × 600 (50 KB) | Bendhoward | The Y-axis units were changed at some point to W/m^2, which is not correct. The units have been changed back to W/m^2/nm, in accordance with the units of the X-axis. | |
| 22:25, 4 Septemba 2014 |  | 800 × 600 (50 KB) | TxBangert | ... changed ^2 to superscript | |
| 22:18, 4 Septemba 2014 | 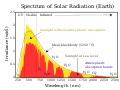 | 800 × 600 (50 KB) | TxBangert | fixed minor errors in how Wikipedia renders svg image | |
| 10:28, 4 Septemba 2014 |  | 800 × 600 (50 KB) | TxBangert | Updated the text to bring it in more in line with other European versions of this graph. W/m2/nm on the y axis is wrong. The units are simply W/m2, the x axis is nm. | |
| 14:50, 4 Maachị 2013 |  | 800 × 600 (50 KB) | Arbeck | Typo corrected - Atmosphere | |
| 15:44, 14 Febụwarị 2013 |  | 800 × 600 (50 KB) | Arbeck | Typo corrected: visible | |
| 15:44, 14 Febụwarị 2013 | 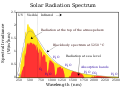 | 800 × 600 (50 KB) | Arbeck | Typo correctedvisible |
Ojiji faịlụ
Ihe ndị na-eso ihe eji Ihu akwụkwọ eme na faịlụ a:
Ejiji failụ zụrụ ọha
Wikis ndi a edeputara na eji kwa failụ a:
- Ihe eji na ca.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na de.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na el.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na en.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na es.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na eu.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na hak.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na hi.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na hu.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na ja.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na mk.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na ms.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na pt.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na sk.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na sl.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na te.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na uz.wikipedia.org
- Ihe eji na vi.wikipedia.org