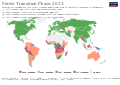
English: Where are countries in the transition today?
If we look at where countries are in their transition today we can understand where we expect to lose and gain forest in the coming decades. Most of our future deforestation is going to come from countries in the pre- or early-transition phase.
Several studies have assessed the stage of countries across the world.. The most recent analysis to date was published by Florence Pendrill and colleagues (2019) which looked at each country’s stage in the transition, the drivers of deforestation but also the role of international trade. `To do this, they used the standard metrics discussed in our theory of forest transitions earlier: the share of land that is forested, and the annual change in forest cover.
In the map we see their assessment of each country’s stage in the transition. Most of today’s richest countries – all of Europe, North America, Japan, South Korea – have passed the turning point and are now regaining forest. This is also true for major economies such as China and India. That these countries have recently regained forests is also visible in the long-term forest trends above.
Across sub-tropical countries we have a mix: many upper-middle income countries are now in the late transition phase. Brazil, for example, went through a period of very rapid deforestation in the 1980s and 90s (its ‘early transition’ phase) but its losses have slowed, meaning it is now in the late transition. Countries such as Indonesia, Myanmar, and the Democratic Republic of Congo are in the early transition phase and are losing forests quickly. Some of the world’s poorest countries are still in the pre-transition phase. In the coming decades this is where we might expect to see the most rapid loss of forests unless these countries take action to prevent it, and the world supports them in the goal.