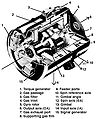
ST-124-M3 inertial platform


ST-124-M3 inertial platform bụ ngwaọrụ maka ịlele ọsọ na àgwà nke ụgbọ elu Saturn V. Ọ bụ Saturn V Instrument Unit, akụkụ dị mita atọ n'ịdị elu (0.91 , 22 n'obosara (6.7 m) nke Saturn V nke dabara n'etiti ọkwa nke atọ (S-IVB) na ụgbọ mbara igwe Apollo. Nkọwa [1] pụtara "tebụl kwụsiri ike" (ST) maka iji ya mee ihe na ọrụ ọnwa (M), ọ nwekwara gimbals atọ.
Ọganihu
[dezie | dezie ebe o si]Ọ bụ nọmba 124 n'usoro ngwaọrụ ndị yiri ya, gụnyere ST-80 (nke e ji mee ihe na Redstone), ST-90 (nke e jiri mee ihe na Jupiter na ụgbọ elu Saturn I), na ST-120 (nke ejiri na Pershing missile). [2] bụ ụmụ nke LEV-3 nke German V-2 rocket. Ọ bụ Marshall Space Flight Center mepụtara ST-124 ma mepụta ya site na Bendix Corporation, Eclipse-Pioneer Division, na Teterboro, New Jersey. O were ndị ikom 9 izu 22 ruo 24 iji jikọta ST-124, na pasent 70 nke oge ahụ ka a na-etinye ihe dị ka wires 3,000. [1]
Akụkọ ihe mere eme
[dezie | dezie ebe o si]The ST-124 stabilized platform was part of the guidance, navigation, and control system of the Saturn V. Data from the ST-124 were used by the Launch Vehicle Digital Computer (another Instrument Unit component) to compare actual flight data to programmed flight plans and to calculate guidance corrections. Though the ST-124 operated all during the mission, its data were not used for guidance while the vehicle was in the atmosphere, where it was subjected to high drag forces. In this region, basically the time of the first stage burn, the vehicle followed a simple preprogrammed flight plan.[2] Frank Cornella delivered the instruments (Gyros and accelerometers) from Teterboro New Jersey to Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville AlabamaTempleeti:Citation Needed.
Nkọwa dị n'ime
[dezie | dezie ebe o si]A tụrụ àgwà nke ụgbọ ala ahụ n'ihe gbasara usoro nhazi nke a kwadoro tupu ịmalite ya na X coordinate kwụ ọtọ, Z coordinate na ntụziaka nke pitch maneuver (n'okpuru, ihe dị ka ọwụwa anyanwụ), na Y coordinate kwụ n'akụkụ abụọ ndị ọzọ, gafee, ihe dịkarịa ala North na South. N'etiti ST-124 bụ ikpo okwu nke e mere n'ụzọ kwụ ọtọ; ya mere aha ahụ bụ "ikpo okwu kwụsiri ike". A na-ejikọta ya site na gimbals atọ nke na-enye ohere ka ụgbọ ala ahụ na-agbagharị, na-agba ọsọ ma na-agbaji ma na-ejide ikpo okwu ahụ n'ime mbara igwe ka ụgbọ ala na-asụgharị n'ụzọ ya.
Ejiri gyros atọ guzoro n'elu ikpo okwu ahụ. Otu tụrụ ntụgharị ọ bụla gbasara axis X, otu gbasara Y, na otu gbasara axis Z. Ha weputara akara nke emere na sekit nzaghachi wee zighachi ya na torquers dị n'ime, etiti na mpụta nke na-emegide ntụgharị ahụ, na-emebi nsonaazụ gyro na idobe ikpo okwu kwụsie ike.
Gimbal dị n'ime bukwara ngwa ngwa atọ, pendulum abụọ, na otu ụzọ prisms. Ihe accelerometer tụrụ n'ọsọ ụgbọ ala n'akụkụ axes X, Y na Z. Ndị LVDC ji arụpụta ha wee tụọ mmegharị ụgbọ ala n'ezie, maka ebumnuche ịnyagharị. A na-eji pendulum ahụ tọọ axis X kwụ ọtọ tupu mmalite ya, a na-ejikwa prisms na-edozi axes Y na Z, obere oge tupu ịmalite. Prisms ahụ gosipụtara ihie infrared ezigara na ST-124 site na theodolite guzoro n'ala 700 ụkwụ site na pad mmalite. A na-ebufe iwu sitere na theodolite site na eriri dị n'ime ụgbọ ala, na torquers na ST-124 iji mee ka ikpo okwu kwụsiri ike gaa na azimuth ziri ezi.
Gyros, accelerometers na pendulums nwere ihe fọrọ nke nta ka ọ bụrụ nitrogen gas bearings na-enweghị friction. Ihe ndị a chọrọ nhazi nke ọma na obere oghere dị n'etiti ebe ndị a na-ebugharị. [5][4] na-ejide nha na nnagide nke 20 microinches (0.5 , [1] na oghere nitrogen jupụtara bụ ihe dịka 600-800 microinches (15-20 μm). [2] Nitrogen banyere na gyros na ihe dị ka 15 psi ma wepụ ya na mbara igwe site na onye na-achịkwa nrụgide na ala nke ST-124 nke meghere na 13 psi. Nnukwu okirikiri ọlaọcha dị n'aka ekpe nke ST-124 nwere nitrogen maka ihe ndị na-ebute ya.
ST-124 gụnyere ọtụtụ ihe mejupụtara beryllium anodized. A họọrọ ihe a maka nkwụsi ike ya, ịdị arọ dị arọ, machinability na nkwụsi ike. Ikpe nke ST-124 bụ cylinder dị mkpụmkpụ, 7.5 in (19 cm) dị elu yana 21 in (53 cm) na dayameta, jiri beryllium mee. A na-emechi ngwụcha nke cylinder ahụ site na ihe mkpuchi aluminom abụọ dị ka hemispherical. E jikwa beryllium mee gimbals na ọtụtụ akụkụ nke gyros na accelerometers.
N'adịghị ka beryllium, nke dị arọ, a na-eji Elkonite eme rotors nke gyros, nke siri ike, nke siri oke. Nke a bụ ụdị ọla kọpa-tungsten, W90/Cu10, iji mee ka ọ bụrụ ihe na-arụ ọrụ. [<span title="There are many grades of Elkonite, so please clarify which one (April 2011)">clarification needed</span>]
Okpomọkụ nke torquers na ngwa eletriki ndị ọzọ dị n'ime ST-124 na-ebufe ya site na mkpuchi jụrụ oyi wuru n'ime mkpuchi aluminum. Ngwakọta nke methanol na mmiri dị na 15 °C (59 °F) ka ekesara n'ime eriri igwe. Okpomọkụ dị n'ime nke ST-124 kwụsiri ike n'ihe dịka 42ºC (108 °F)..
-
Ihe osise nke ST-124M site na ntuziaka teknụzụ Instrument Unit
-
Ụdị ST-124 na nchịkọta nke National Air and Space Museum, Washington, DC
-
Ihe osise nke ST-124 gimbals
-
ST-124 na onye na-ahụ maka ọrụ
-
ST-124 na ngosi na Honeywell Defense Avionics Systems na Teterboro, NJ
-
AB5-K8 gyro inner cylinder assembly
-
AB5-K8 na-ebute gas gyro
-
AB5-K8 gyro
-
Ihe osise nke AB5-K8 gyro
-
gimbals nke dị n'ime na nke dị n"etiti
Edensibia
[dezie | dezie ebe o si]- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Globe-shaped platform keeps Apollo on target", The Bendix Corporation Newsbureau.
- ↑ Haeussermann 1970, p. 1.
Akwụkwọ
[dezie | dezie ebe o si]- Bilstein (1980). "8: From Checkout to Launch: The Quintessential Computer", Stages to Saturn: A Technological History of the Apollo/Saturn Launch Vehicles, NASA History Series. NASA, 243–253. NASA SP-4206; 97N-15592. ISBN 0-16-048909-1.
- Nke a nwere ọnụ ọgụgụ doro anya karịa ọtụtụ akwụkwọ PDF banyere IU, na-enye echiche kachasị mma nke ime gyros na gas bearings.
Ịgụ ihe ọzọ
[dezie | dezie ebe o si]- (1 November 1968) Astrionics System Handbook: Saturn Launch Vehicles. IBM Corporation, Astrionics Laboratory. MSFC No. IV-4-401-1; IBM No. 68-966-0002; 70N-70002.
- Akụkọ mbụ, na mgbakọ na mwepụ, kama ịkọwapụta, nke ST-124. N'ụbọchị a, ST-124 bụ echiche 4-gimbal, ebe ụdị nke na-efe efe nwere naanị 3 gimbals.
- Mgbasa ozi metụtaraST-124-M3 inertial ikpo okwuna Wikimedia Commons